Search Posts
Recent Posts
- Real Estate in RI: Seaside waterfront communities are all the rage. Who’s buying – Emilio DiSpirito June 6, 2025
- Outdoors in RI: 2A votes, Charter Yachts, active summer programs, garden tours, aquatic weeds… June 6, 2025
- All About Home Care, with two Rhode Island locations, closing after 22 years in business June 6, 2025
- GriefSPEAK: Angel wings with footprints – Mari Nardolillo Dias June 6, 2025
- Rhode Island Weather for June 6, 2025 – Jack Donnelly June 6, 2025
Categories
Subscribe!
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.

RI Needs Overhaul of Developmental Disabilities System
RI needs overhaul of Developmental Disabilities system to comply with 2014 agreement
By Gina Macris, Developmental Disabilities News, contributing writer
During the next three years, Rhode Island must completely restructure its services for adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities and increase financial support accordingly to fully comply with a federal civil rights consent decree by the 2024 deadline.

That is the conclusion of an independent federal court monitor, A. Anthony Antosh, in an Oct. 7 report to Chief Judge John J. McConnell, Jr. of the U.S. District Court.
At McConnell’s direction, Antosh says he’s also working on a dollar figure for the cost of compliance, using an outside $1.1 million analysis of existing services commissioned by the state itself.
The state agreed, under the consent decree in 2014, to end its reliance on sheltered workshops and group day care centers and instead put adults with developmental disabilities in the driver’s seat when choosing a path in life, with an emphasis on regular employment and participation in community activities.
The last sheltered workshop closed in 2018, but many of the other goals of the consent decree have remained elusive, and Judge McConnell has grown impatient with a lack of funding he says is necessary to lay the foundation for compliance by the time federal oversight is scheduled to expire in 2024.

John J. McConnell, Jr. “If anybody couldn’t tell, I am obsessed with the issue of funding as essential for us to get there,” McConnell said during a virtual hearing in July.
“If we don’t come up with a way to systemically support the (service) providers, then the whole thing will be meaningless,” McConnell said.
He has said he is prepared to tell the state to “find the money” to comply with the consent decree. State officials who control the purse strings must participate in the redesign of services, the judge has said.
In the most recent monitor’s report, Antosh set the tone for his recommendations by saying that compliance is “not found in a narrow analysis of the benchmarks of the Consent Decree, but is rooted in defining the structural changes that need to occur in order that the goals of the Consent Decree can be achieved.”
In bold print, he highlighted the fact that the outside analysis of the existing system found that most of the private service providers are “fragile and profoundly undercapitalized.”
In a separate report, the state responded to a court order that it address 16 fiscal and administrative barriers to the integration of people with developmental disabilities into their communities as mandated by the consent decree. The summary is the first of six progress reports the state must make to Judge McConnell by next June on its planning effort for long-range reform.
In its report, the state set a deadline of March, 2022 to overhaul its fiscal system. The changes include the elimination of three practices that for years have been identified as problematic by families and providers:
- staffing ratios that discourage community integration, so that in some cases, one worker must supervise up to five people on an outing, whether or not those people want to be there.
- documentation of staff time in 15-minute increments, which providers say diverts significant resources that otherwise could be used for direct services.
- Allocation of a certain percentage of services for segregated facility-based activities.
Alluding to the budget uncertainties caused by the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic, the state’s seven-page summary cautions that the planning efforts are “dependent upon the continuation of current state staffing and budgetary levels.”
Monitor’s Budget For Reform Coming “Soon”
McConnell has asked Antosh to analyze current funding and make a dollars-and-cents recommendation for the cost of implementing the needed comprehensive changes.
Antosh said that report will be completed “soon.” He said he has begun that work, relying primarily on data drawn from an 18-month study done by the New England States Consortium Systems Organization (NESCSO) for the state’s disability agency.
The 143-page NESCSO study presented a number of findings and options for change but made no recommendations, at the behest of the Department of Behavioral Healthcare, Developmental Disabilities and Hospitals.
Antosh said there is a need for systemic restructuring of existing services and supports, which are now “essentially based on group activities that occur in a blend of facility and community settings.”
The situation is exacerbated by a difficulty in recruiting and retaining high quality staff and by the COVID-19 pandemic, which in emphasizing the health risks of large gatherings has “reinforced the diminishing value of facility-based group services,” Antosh said.
The pandemic also has led to a setback in the progress made in the area of employment for adults with developmental disabilities. In June, as the state was beginning to reopen, only 31 percent of those who previously held jobs were still actively employed, Antosh said. (Some on furlough have since returned to work.)
Among work crews hired for large scale commercial cleaning or laundry operations and the like, only about half were working, he said.
The statistics underline a need for “new and intensified approaches to job development,” he said. “What is needed is a new model for providing supports that is more individualized, community based, and uses funds and supports from an increased variety of sources,” including the state’s Department of Labor and Training, Antosh said.
Family Hesitation About Integration
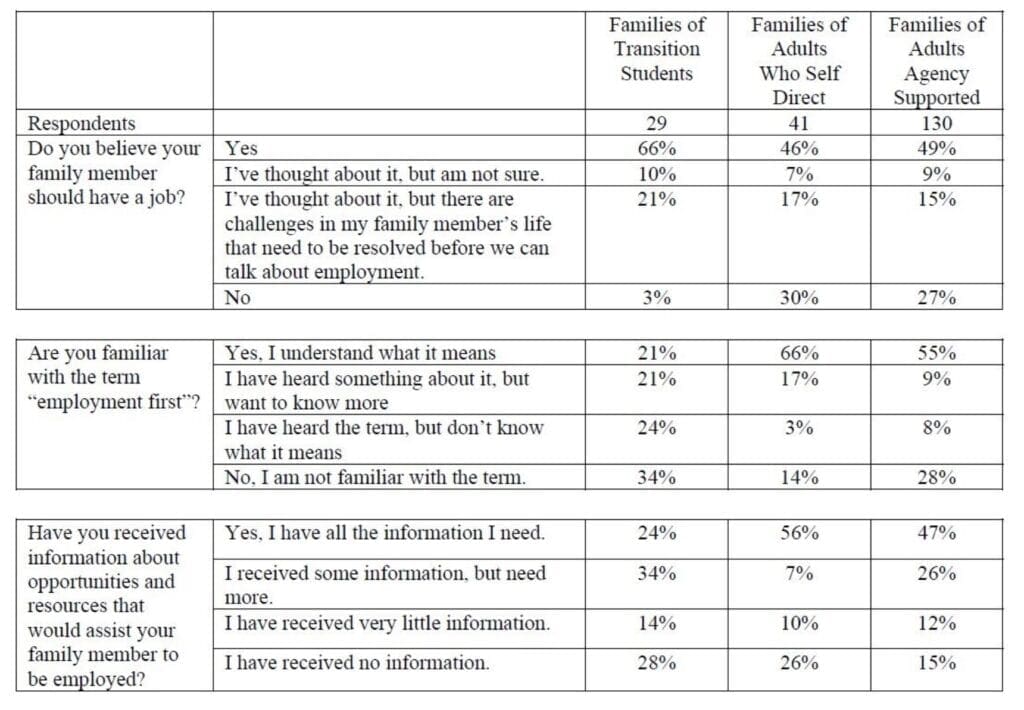
While the gears of state government are focused on moving Rhode Island into compliance with the federal government’s mandate of integrating individuals with developmental disabilities into the larger community, more than a third of the families with an adult son or daughter who would benefit say they oppose or are not yet convinced that the push toward employment is worthwhile.
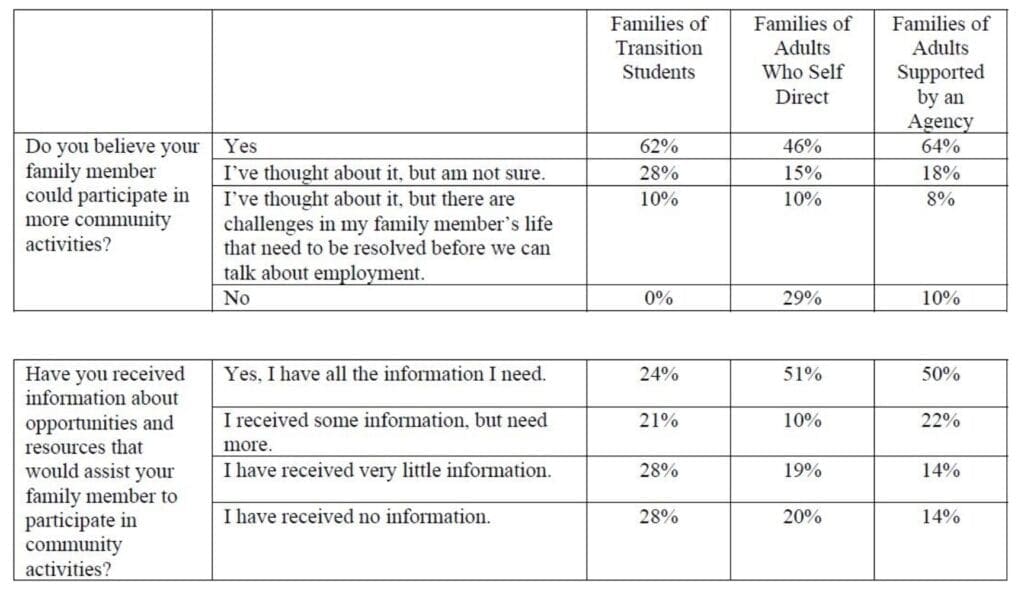
The pandemic aside, significant numbers of families also express opposition or hesitation about their loved ones’ increased participation in community activities.
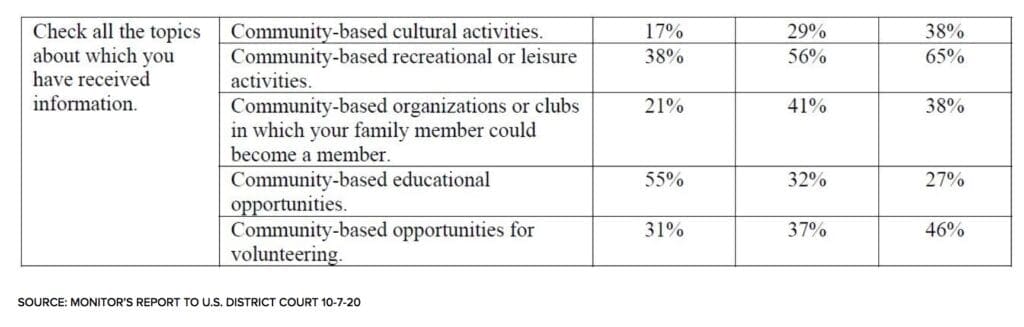
For Antosh, who included survey results of families as part of his report, the statistics underscore the need for adolescents to experience work-related and social activities in their communities as part of their education and for families to receive more information about the breadth of available opportunities.
It is perhaps most telling that among families of high school students, who are more likely than their older peers to have had internships and community experiences as part of their education, only 3 percent were opposed to jobs for their sons and daughters and 10 percent said they weren’t sure. Two thirds of families of adolescents said they believed the young people should have jobs as adults. Other parents of high school students – about one in five- said their son or daughter had to deal with other challenges before turning to employment. This is typically the case for those with chronic health problems.
The 2014 statewide consent decree draws its authority from the Integration Mandate of the Americans With Disabilities Act, which was reinforced by the Olmstead decision of the U.S. Supreme Court. The high court said that states must deliver services to all persons with disabilities in the most integrated setting that is therapeutically appropriate, and it presumed that setting to be the community.
In 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice found that the state violated the Integration Mandate by funneling high school students from segregated educational programs with low expectations to a lifetime of isolation in sheltered workshops and day care programs. In signing the consent decree, the state agreed to correct the violations by 2024. (A preliminary case against the state and the city of Providence in 2013 was merged into the statewide consent decree a year ago after Judge McConnell found the city and its school department had turned around a segregated high school program for students with developmental disabilities, leaving only the state as the defendant.
Antosh outlined several overarching features of successful implementation of the consent decree, including these:
- Each person will have the supports necessary to enjoy a self-determined, self-directed life based on work and non-work activities in the community.
- Private provider agencies will have the funding, staffing and other resources they need to meet the support needs of all persons receiving funding through the Division of Developmental Disabilities.
- Every adolescent and adult with intellectual or developmental disabilities will have the information and guidance they need to navigate a simpler and more efficient system of services.
- All adolescents and young adults leaving school will have had enough transitional work-related and non-work experiences in the community to make informed choices about jobs and careers, as well as a plan to direct their own programs or sign on with a provider organization.
Antosh recommended that the state develop a three-year budget strategy, beginning July 1, 2021, to “stabilize” developmental disability services and provide sufficient funding to implement the consent decree.
The monitor’s recommendations include a new, formal role for the Department of Labor and Training (DLT), which until now has not been a part of the multi-agency state team responsible for official responses to the court.
Antosh said DLT should immediately join BHDDH, the state Department of Education, the Department of Human Services, and the Executive Office of Health and Human Services in working on consent decree compliance.
DLT also should include all teenagers and adults with developmental disabilities in the workforce initiatives it administers, the monitor said.
By Jan. 1, 2021, the state should create an “Employer Task Force” to promote employment of those with developmental disabilities, Antosh said. The task force would identify relevant workforce trends and advise state officials and provider organizations about ways to reach out to prospective employers and offer employers incentives and support.
By April 1, 2021, the state must identify every possible source of funding that could support the consent decree and describe ways these sources can be “braided” to support the various requirements of the agreement.
As for private providers, the backbone of the service system, Antosh set a deadline of April 30, 2021 for them to develop action plans for the future. There are 36 provider agencies, most of them offering both day and residential services. In their plans, providers should redefine the support area that will be their focus, address consent decree issues, make budget projections and include internal quality improvement programs.
Just as the state has established five workgroups to address fiscal and administrative problems, Antosh recommended the state create additional issue-oriented work groups whose members are drawn from the ranks of state officials and community organizations, like the Employment Force Task Force.
One group would develop strategies to stabilize the workforce by increasing salaries, elevating professionalism through training, and creating a career ladder.
Other groups would address specific plans for:
- putting individuals at the center of mapping out long range and short-term goals for their future and strategies for achieving them
- ensuring young people have a smooth transition from high school to adult services,
- creating new models for providing services and supports for employment and community-based activities.
- enhancing the use of technology as a support strategy
- Developing alternative transportation options, including stipends that allow individuals to arrange their own rides
- Improving outreach to families, including those speak languages other than English and come from diverse cultures.
To read the full monitor’s report, click here. To read the state’s report, click here.
Photos by Anne Peters

Gina Macris is a career journalist with 43 years’ experience as a reporter for the Providence Journal in Providence, RI. She retired in 2012. During her time at the newspaper, she wrote two series about her first-born son, Michael M. Smith. Both series won prizes from the New England Associated Press News Executives Association. Michael, now in his 30s, appears on the cover page, in front of the Rhode Island State House.
