Search Posts
Recent Posts
- Rhode Island Legislature Highlights Accomplishments for the 2025 Session June 25, 2025
- Sports in RI: Cody Tow, Volleyball Past, Present and Into His Future – John Cardullo June 25, 2025
- Need a Break? Time for Sour Grapes – Tim Jones June 25, 2025
- Rhode Island Weather Forecast for June 25, 2025 – Jack Donnelly June 25, 2025
- It is what it is: Commentary on 6.25.25 with Jen Brien June 25, 2025
Categories
Subscribe!
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.

Community specific, RI Healthy Aging Data Report a boon for officials, policymakers – Herb Weiss
By Herb Weiss, contributing writer on aging
In an era of tightening budgets and shrinking federal and state resources for aging programs, legislators, service providers, and advocates now have access to vital data that can help identify and address the unmet needs of older adults in their communities.
Just over a week ago, the Gerontology Institute at the University of Massachusetts Boston released the latest Healthy Aging Data Reports (HADR), funded by the Point32Health Foundation. These reports offer a comprehensive, neighborhood-level view of aging in America—insights often unavailable from other sources.
Rhode Island’s updated report, released on May 1, 2025, follows previous editions published in 2016 and 2020. This year’s release also includes updates for Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire, and introduces a first-time report for Maine. The HADR team is now expanding its reach to additional regions, including parts of the Deep South (such as Mississippi) and the West (including Wyoming).
“This is what’s magical about our report: we provide data at very local levels,” says Dr. Elizabeth Dugan, principal investigator and associate professor of gerontology at UMass Boston. “That empowers local advocates, helps policymakers make smarter investments, and allows philanthropists to assess the impact of their contributions,” she says.
The Rhode Island report features 41 community profiles—covering each city and town, along with two neighborhoods in Providence. Drawing on data from the U.S. Census Bureau, Medicare Summary Beneficiary Files, the CDC’s Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, and state health departments, the report highlights disparities that may be hidden in broader state- or county-level statistics.
“What’s powerful about this approach is that we can observe health outcomes that vary dramatically even within a 10-minute walk in the same city,” adds Dugan.
Spotlight on Rhode Island
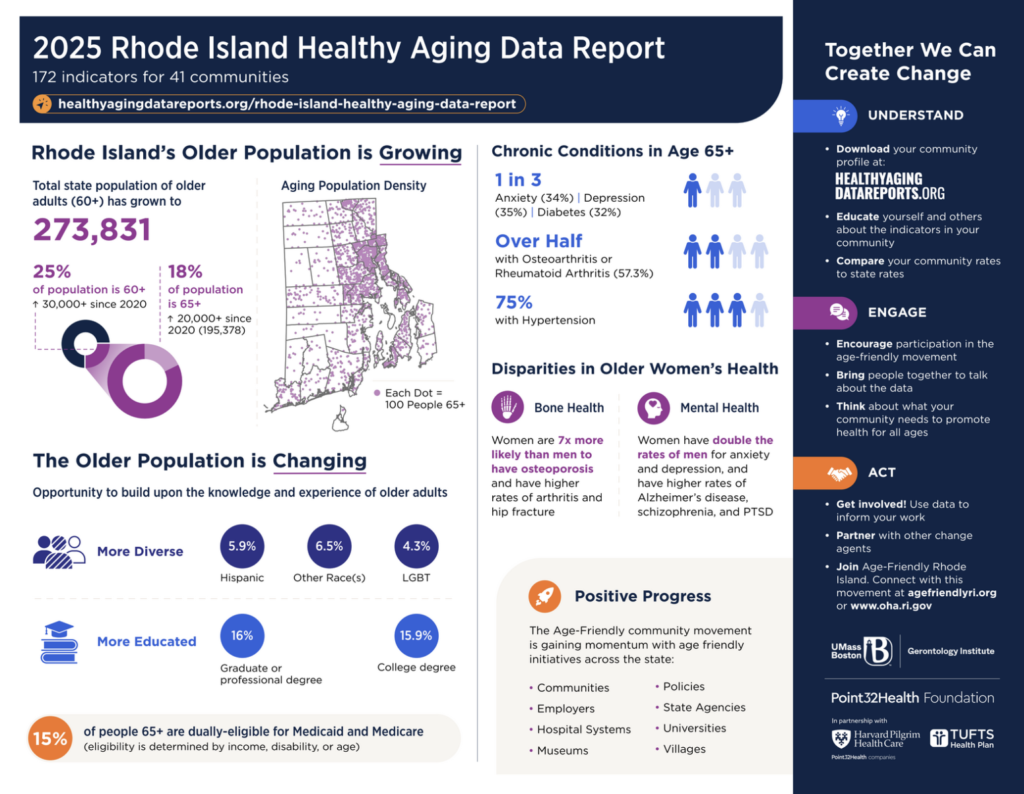
Several key findings emerged from the 2025 Rhode Island report:
- Health: Rhode Island ranks highest in New England for rates of high cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, ischemic heart disease and peripheral hearth disease, stroke, multiple chronic conditions (four or more), and anxiety disorders.
- Gender Disparities: Women experience anxiety and depression at rates 15% higher than men and are also more likely to suffer from Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and PTSD.
- Housing: Roughly 39% of older renters spend more than 35% of their income on housing. Additionally, 46% of Rhode Islanders aged 65 and older report annual incomes under $50,000.
“The Rhode Island Healthy Aging Data Reports are invaluable,” says Maureen Maigret, Policy Advisor for the Senior Agenda Coalition of Rhode Island and a member of several state aging commissions. “They provide essential data down to the ZIP code level, which is useful for legislative testimony, policy recommendations, program planning, and grant writing.”
With Rhode Island’s older adult population rising from 16.5% in 2020 to 18% in 2025, this data is more critical than ever. “The report shows how age and racial diversity vary widely across communities,” Maigret says, noting that in some smaller towns, older adults now make up over 30% of the population.
Maigret notes that availability of localized data helps municipalities develop comprehensive plans and adopt age-friendly strategies. Interactive maps within the report allow comparisons with state averages, making it easier to target resources where they are most needed.
The report also reveals demographic shifts, including a rise in the Hispanic older adult population—from 4.9% in 2020 to 5.9% in 2025. “There are significant racial and ethnic disparities in health outcomes,” says Maigret. “Black and Hispanic older adults are more likely to be dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid and to be enrolled in Medicare managed care,” she says.
As lawmakers navigate complex budget negotiations and potential changes to federal programs such as the Administration for Community Living, Medicaid, and the CDC, Maigret stresses the importance of leveraging this data in decision-making.
“Despite the growth in our older population and increasing reports of elder abuse, neglect, and substandard nursing home care, the Office of Healthy Aging’s budget has remained relatively flat,” she warns. “With half of its funding coming from the federal government, proposed cuts could seriously undermine vital programs such as the Long-Term Care Ombudsman,” she adds.
The report also shines a light on mental health, showing high rates of depression and anxiety—especially among older women. Maigret believes this supports increased investment in the 988 mental health crisis line and other behavioral health services.
Another notable trend is the continued shift toward Medicare managed care, now covering more than half of Rhode Islanders aged 65 and older. While rates of arthritis and depression have increased, the report also notes a decline in nursing home stays, inpatient admissions, emergency room visits, and several chronic conditions such as diabetes, COPD, hypertension, and heart disease.
Since the 2020 report, communities have taken meaningful steps to support aging in place. “The Village Common of RI has built age-friendly communities that enable older adults to live independently with the care and resources needed to promote health and well-being,” says Maigret. “There are now 11 local villages across 14 communities, supported by trained volunteers who help members stay connected and independent.”
Data Driving Policy and Innovation
Marie E. Cimini, MSW, Director of the Rhode Island Office of Healthy Aging, says the HADR report has broad implications. “As a state agency, we must lead with policies that prioritize inclusion, access, and dignity throughout the aging journey.”
“The report reinforces our commitment to advancing the goals outlined in the RI 2030 Plan, especially around expanding in-home care, supporting workforce development, and strengthening behavioral health services,” Cimini continues. “But it also challenges us to go further—to integrate aging into every aspect of public life and ensure that the voices of older adults inform policy at every level.”
For Meghan Grady, Executive Director of Meals on Wheels of Rhode Island (MOWRI), one of the most important takeaways is the persistence of health disparities, particularly in managing chronic conditions. Grady supports legislation introduced by Sen. Victoria Gu (D-Dist. 38) and Rep. Justine Caldwell (D-Dist. 30) to integrate medically tailored meals into healthcare delivery. “This report validates our advocacy,” she says. “Food is a fundamental part of care, especially for aging populations facing health disparities.”
The HADR report is also proving instrumental for nonprofit organizations. “We use the data in community presentations, grant proposals, and to guide our work in promoting health equity,” says Deb Burton, Executive Director of RI Elder Info. “With so much uncertainty around policy and funding for programs that impact older adults and caregivers, this data helps us identify where changes will have the greatest impact,” she says.
James Connell, Executive Director of Age-Friendly RI, agrees. “The Healthy Aging Data Report is extraordinarily helpful for nonprofits across sectors. I used it to support funding for a home-share program that pairs older homeowners with individuals facing housing insecurity—a creative approach to our state’s housing crisis,” he says. “The ’25 Healthy Aging Report provides vital indicators of older adult well-being that are essential for policymaking, intentional planning, and program development,” says Connell. “The data highlight serious concerns about the mental and emotional health of our community, with one in three Rhode Islanders experiencing anxiety and/or depression.” Connell also emphasizes the report’s finding that women are disproportionately affected, calling it “a clear call to action for improved screening and more accessible treatment options.”
Greg Shell, Chair of the Point32Health Foundation Board of Directors, emphasizes the value of data in shaping policy. “When we use data to guide our work, we can change policies and practices, engage communities, and highlight what truly matters,” he says. “These reports are essential tools in making New England a better place to grow up and grow old.”
The research team behind the Healthy Aging Data Reports includes: Principal Investigator Elizabeth Dugan, PhD, along with Nina Silverstein, PhD; Qian Song, PhD; Taylor Jansen, PhD; Jay Lee, PhD; Yan-Jhu Su, PhD; Han Lin, PhD; Shan Qu, MS; Tiffany Tang, BS; Jeannine Johnson, PhD; Amanda Cox, MS; and Mengshi Liu.
To access the 2025 Rhode Island Healthy Aging Data Report, visit https://healthyagingdatareports.org/ri/rhode-island-healthy-aging-data-report.
___
To read more articles by Herb Weiss, go to: https://rinewstoday.com/herb-weiss/

Herb Weiss, LRI ‘12, is a Pawtucket-based writer who has covered aging, healthcare, and medical issues for over 45 years. To purchase his books, Taking Charge: Collected Stories on Aging Boldly and its two sequels, visit herbweiss.com.
To purchase his books, Taking Charge: Collected Stories on Aging Boldly and two sequels, compiling weekly published articles, go to herbweiss.com – or purchase from Amazon.

